Android banking trojans: How they steal passwords and drain bank accounts
For the most popular operating system in the world—which is Android and it isn’t even a contest—there’s a sneaky cyberthreat that can empty out a person’s bank accounts to fill the illicit coffers of cybercriminals.
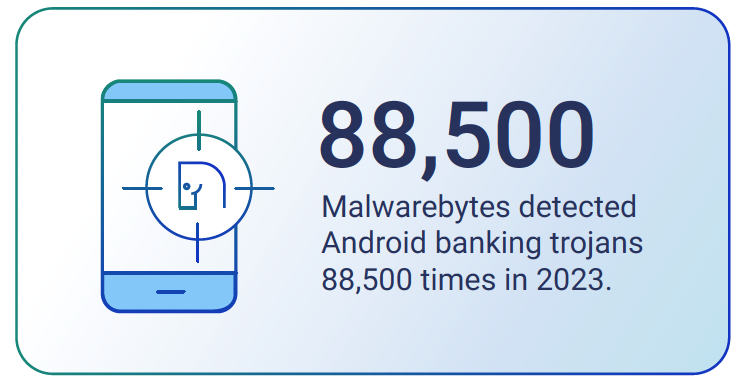
These are “Android banking trojans,” and, according to our 2024 ThreatDown State of Malware report, Malwarebytes detected an astonishing 88,500 of them last year alone.
While the 2024 ThreatDown State of Malware report focuses heavily on the corporate security landscape today, make no mistake: Android banking trojans pose a serious threat to everyday users. They are well-disguised, hard to detect in regular use, and are a favorite hacking tool for cybercriminals who want to automate the theft of online funds for themselves.
What are Android banking trojans?
The idea behind Android banking trojans—and all cyber trojans—is simple: Much like the fabled “Trojan Horse” which, the story goes, carried a violent surprise for the city of Troy, Android banking trojans can be found on the internet disguised as benign, legitimate mobile apps that, once installed on a device, reveal more sinister intentions.
By masquerading as everyday mobile apps for things like QR code readers, fitness trackers, and productivity or photography tools, Android banking trojans intercept a person’s online interest in one app, and instead deliver a malicious tool that cybercriminals can abuse later on.
But modern devices aren’t so faulty that an errant mobile app download can lead to full device control or the complete revelation of all your private details, like your email, social media, and banking logins. Instead, what makes Android banking trojans so tricky is that, once installed, they present legitimate-looking permissions screens that ask users to grant the new app all sorts of access to their device, under the guise of improving functionality.
Take the SharkBot banking trojan, which Malwarebytes detects and stops. Last year, Malwarebytes found this Android banking trojan hiding itself as a file recovery tool called “RecoverFiles.” Once installed on a device, “RecoverFiles” asked for access to “photos, videos, music, and audio on this device,” along with extra permissions to access files, map and talk to other apps, and even send payments via Google Play.
These are just the sorts of permissions that any piece of malware needs to dig into your personally identifiable information and your separate apps to steal your usernames, passwords, and other important information that should be kept private and secure.
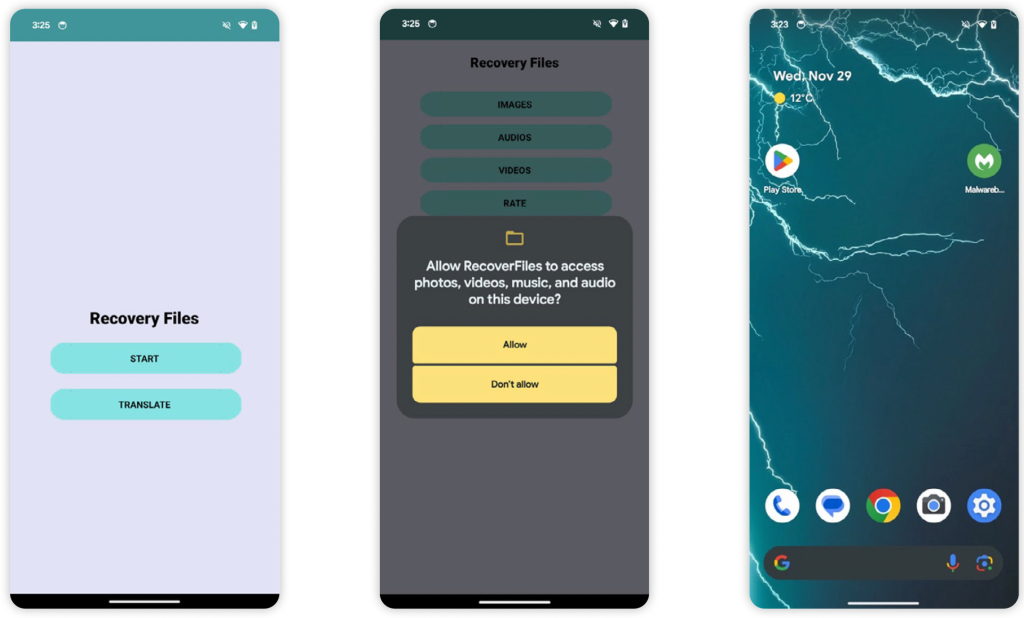
Still, the tricks behind “RecoverFiles” aren’t yet over.
Not only is the app a clever wrapper for an Android banking trojan, it could also be considered a hidden wrapper. Once installed on a device, the “RecoverFiles” app icon itself does not show up on a device’s home screen. This stealth maneuver is similar to the features of stalkerware-type apps, which can be used to non-consensually spy on another person’s physical and digital activity.
But in the world of Android banking trojan development, cybercrminals have devised far more devious schemes than simple camouflage.
Slipping under the radar
The problem with the Ancient Greeks’ Trojan Horse strategy is that it could only work once—if you don’t sack Troy the first time, you better believe Troy is going to implement some strict security controls on all future big horse gifts.
The makers of Android banking trojans have to overcome similar (and far more advanced) security measures from Google. As the Google Play store has become the go-to marketplace for Android apps, cybercriminals try to place their malicious apps on Google Play to catch the highest number of victims. But Google Play’s security measures frequently detect malware and prevent it from being listed.
So, what’s a cybercriminal to do?
In these instances, cybercriminals make an application that is seemingly benign, but, once installed on a device, executes a line of code that actually downloads malware from somewhere else on the internet. This is how cybercriminals recently snuck their malware onto Google Play and potentially infected more than 100,000 users with the Anatsa banking trojan.
What was most concerning in this attack was that the malicious apps that made it onto the Google Play store reportedly worked for their intended purposes—the PDF reader read PDFs, the file manager managed files. But hidden within the apps’ coding, users were actually downloading a set of instructions that directed their devices to install malware.
These malicious packages are sometimes called “malware droppers” as the apps “drop” malware onto a device at a later time.
What does it all mean for me?
There’s a lot of technical machinery at work inside any Android banking trojan that is put in place to accomplish a rather simple end goal, which is stealing your money.
All the camouflage, subterfuge, and hidden code execution is part of a longer attack chain in which Android banking trojans steal your passwords and personally identifiable information, and then use that information to take your money.
As we wrote in the 2024 ThreatDown State of Malware report:
“Once it has accessibility permissions, the malware initializes its Automated TransferSystem (ATS) framework, a complex set of scripts and commands designed to perform automated banking transactions without user intervention. The ATS framework uses the harvested credentials to initiate unauthorized money transfers to accounts held by the attacker. This mimics real user behavior to bypass fraud detection systems.”
Staying safe from Android banking trojans
Protecting yourself from Android banking trojans is not as simple as, say, spotting grammatical mistakes in a phishing email or refusing to click any links sent in text messages from unknown numbers. But just because Android banking trojans are harder to detect by eye does not mean that they’re impossible to stop.
Malwarebytes Premium provides real-time protection to detect and stop Android banking trojans that are accidentally installed on your devices. It doesn’t matter if the banking trojan is simply a malicious app in a convenient package, or if the banking trojan is downloaded through a “malware dropper”—Malwarebytes Premium provides 24/7 cybersecurity coverage and stops dangerous attacks before they can be carried out.
We don’t just report on threats—we remove them
Cybersecurity risks should never spread beyond a headline. Keep threats off your devices by downloading Malwarebytes today.
